Signor ALITO ... Cattivo?
dott. Fiorenzo Fraschina • 14 febbraio 2024
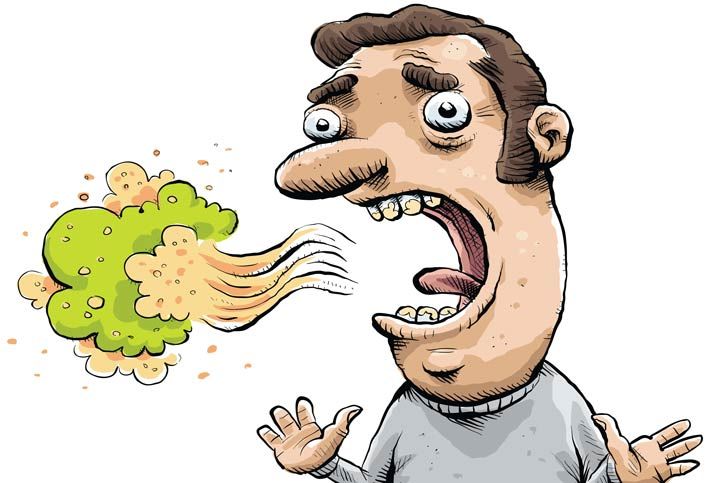

L’alito cattivo crea disagio a chi ci sta vicino e mina il nostro benessere.
L’alitosi è dovuta a componenti sulfuree prodotte dai batteri che decompongono i resti di cibo e i tessuti morti nella nostra bocca. Tra le cause troviamo: la placca, le carie, la parodontite, il tabagismo , il digiuno o anche a seguito di un estrazione.
Rimuovere regolarmente i batteri responsabili del problema permette di eliminare l ‘alitosi!
Se anche tu vuoi avere più informazioni e dettagli per migliorare questo fastidioso problema vieni a farci visita, sapremo consigliarti al meglio.
Bruxism - simply put, the habit of grinding or clenching the teeth - consists of more or less intense activity of the masticatory muscles, which occurs mainly during sleep. Here are some important tips. Many people grind or clench their teeth: an estimated one-fifth of the population suffers from bruxism. In some cases the teeth may be damaged and, in more sensitive people, cause headaches, jaw or neck pain. However, some people also clench their teeth during the day, for example, when they are tense and need to concentrate (in this case we speak of bruxomania). In cases of intense bruxism, up to 100 pounds of pressure is exerted on the jaw. The most frequent cause is stress. Usually the concentration of the masticatory muscles is caused by stress or psychic overload. During sleep we tend, in fact, to process stress by "grinding" our daily problems. In some cases, antidepressants or substances such as alcohol can also cause bruxism. One thing is certain: rubbing the surfaces of the teeth results in progressive wear of the teeth, sometimes even fractures. In cases of intense bruxism, teeth can become particularly sensitive and mobile. Other disorders also occur in the temporomandibular joint and at the level of the masticatory muscles, resulting in facial pain and the appearance of headaches. Therapy Therapy involves applying a so-called "night splint" (Michigan ferula), which does not inhibit bruxism but protects the teeth and prevents pain, allowing the muscles to relax. Many people are unaware that they grind their teeth. If you find out that your partner (or your child) suffers from bruxism, make him or her aware of the problem right away so that they can take action before damage to the teeth arises Reimbursement of treatment for a bruxism problem Only diagnostic therapies are recognized under the basic health insurance; however, the costs of making the bite and the dental laboratory are excluded. If the Michigan plate becomes necessary as a result of an accident (Art. 31 KVG, e.g., as a result of so-called whiplash), the health insurance reimburses all costs.

Fear of the dentist is very common; often this phobia causes one to reschedule important checkups and treatments, thus aggravating one's health status. Those suffering from an acute form of dentophobia will certainly have experienced feelings during dental visits that are manifested by states of panic accompanied by tachycardia, sweating, and nausea. Only a very small percentage of people are affected by this most severe form of dentophobia, but at the same time there is a very significant number of people who are afraid to go to the dentist for a wide variety of reasons: fear of the anesthesia needle, feeling of suffocation during treatment or while taking impressions, very low pain threshold, traumatic experiences suffered as a child. The difficulty of making it to the dentist can over time have negative effects on people's health; the state of tissue health worsens leading to tooth loss, persistent pain, bad breath, decreased self-confidence due to a dental appearance that is no longer "pleasing." A beautiful smile is the best calling card we can show when we present ourselves, which is why today we can overcome dentist phobia thanks to conscious sedation.
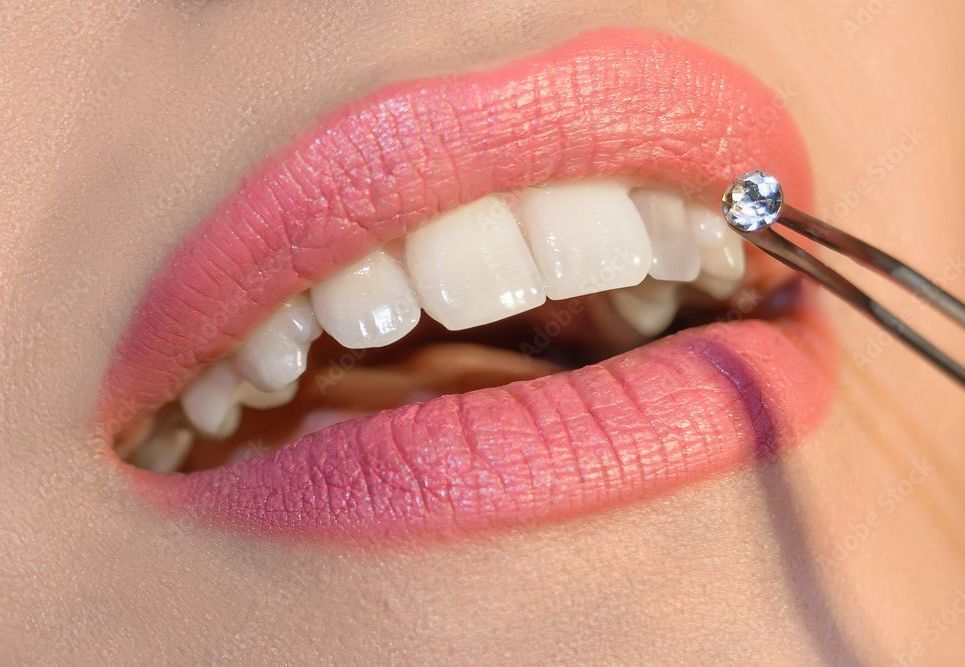

Some people like...shiny. Dental jewelry especially appeals to young women. But what needs to be paid attention to? Glitter or small stones are glued onto teeth with a special product and can be removed quite easily. This kind of jewelry is considered not very dangerous, provided, however, that those who wish to wear them have them applied properly, take care of their oral hygiene, and have regular checkups by their dentist. Dental jewelry should be applied by a dentist, who first checks whether oral health and hygiene are sufficient and whether the enamel on which it will be applied is healthy. The dentist bonds the jewelry with a specific product, also used for white fillings. Is parental consent needed? If a minor wants to decorate their teeth with a glitter, they must have parental consent. Although the application of these jewels does not represent any difficulty, it is still a small intervention on the teeth. It should be pointed out that the placement of gemstones such as diamonds (real glitter) is possible, but it should be known that in order to attach them, it is necessary to drill slightly into the healthy tooth to allow the tip to fit. At our practice we have chosen to apply Swarowski brand glitter. For any information or application of glitter we gladly remain at your disposal and you can contact us at 091/921.01.71

The 77-year-old patient has front teeth with numerous interproximal (between teeth) and collar fillings. This situation no longer satisfies the patient who would like a younger smile. The 77-year-old patient has front teeth with numerous interproximal (between teeth) and collar fillings. This situation no longer satisfies the patient who would like a younger smile. We performed a smile "facelift" by first proposing a sustained whitening with the product ZOOM2 and in a second phase we made 6 ceramic veneers on the upper teeth. The result obtained is truly amazing and the patient is 100% satisfied, happy that even at an advanced age one can have a "facelift" of one's smile. For any information or glitter applications we gladly remain at your disposal and you can contact us at 091/921.01.71

It may happen that following the loss of a tooth due to causes such as trauma, an 'infection, or the extraction of a tooth that occurred long ago, the conditions for it to be replaced by the placement of an artificial root (implant) are no longer met. In fact, the placement of an implant requires an adequate amount of bone to allow for a good fit and durability. In the case of a bone defect, reconstruction can be done by grafting autologous bone taken mostly from the jaw or in cases of minor defects by simply adding a bone substitute. Bone loss varies from one patient to another, and depending on the situation, the simplest and most appropriate treatment is found. If you too need a tooth replacement and would like information about treatment options, you can contact us at 091/921.01.71
C’è chi ha avuto esperienze passata spiacevoli, chi teme l’ago dell’anestesia, chi il suono e le vibrazioni del trapano, chi è semplicemente in imbarazzo per lo stato dei propri denti e poi chi ha semplicemente paura del dolore. Rilassati! C’è chi ha avuto esperienze passata spiacevoli, chi teme l’ago dell’anestesia, chi il suono e le vibrazioni del trapano, chi è semplicemente in imbarazzo per lo stato dei propri denti e poi chi ha semplicemente paura del dolore. Il semplice pensiero della visita dal dentista può rilevarsi un incubo. Ma rischiare di trascurare placca, carie e altre problematiche potrebbe portare a un serio peggioramento. Quindi, come affrontare la paura di una visita dentistica? 1. Fai una lista. Sembrerebbe inutile e banale, ma spesso mettere per iscritto un problema rende la soluzione più semplice. Fai una lista delle cose che non ti piacciono del dentista: i rumori, gli odori, la paura di sentire dolore. 2. Mostra la lista al tuo dentista. Scoprirai che alcune procedure possono essere rese meno fastidiose di quello che sembrano. 3. Tecniche di rilassamento. A casa, prima della visita, così come nello studio dentistico, puoi utilizzare la tecnica di rilassamento che ti piace di più. Cerca di distrarti facendo cose piacevoli prima della visita. 4. Sulla poltrona del dentista non devi per forza ascoltare i rumori degli strumenti. Chiedi al dentista se puoi metterti degli auricolari per ascoltare un po’ di musica che ti distragga. 5. Prova a chiudere gli occhi. Le luci intense e la vista dello strumentario aumentano l’ansia dei pazienti. Con gli occhi chiusi, cerca di pensare a cose piacevoli in una sorta di piccola meditazione: ciò renderà la visita meno pesante per te. “Proprio non ce la faccio, continuo ad avere paura del dentista.” Non preoccuparti! Prova la sedazione cosciente. La sedazione cosciente è una miscela di protossido d’azoto e d’ossigeno che viene somministrata per mezzo di una mascherina nasale a delle concentrazioni personalizzate secondo necessità. L’effetto analgesico e sedativo si avverte già dopo pochi respiri con una sensazione di rilassatezza e distensione. Il paziente rimane comunque sempre pienamente cosciente e vigile durante tutto il trattamento. Al termine della cura viene somministrato per 5 minuti dell’ossigeno puro e questo permette di lasciare lo studio dentistico da solo e in grado di guidare.